As we all know, every machine knife wears out at some point. Despite our best efforts to resharpen machine knives to get the most life from them, at some point the wear and tear to the cutting edge is just too much to get more from the knife – it’s spent, it’s done, it’s time to be retired. You find yourself asking: “Is steel recyclable? Can I recycle my old, worn-out blade?” The simple answer is yes.
Steel can be recycled and reused, which makes it a sustainable material. Recycling steel reduces the need for extracting new iron ore, which conserves natural resources and decreases energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with the production of new steel. Proper steel disposal from your manufacturing processes also reduces the environmental footprint of your facility.
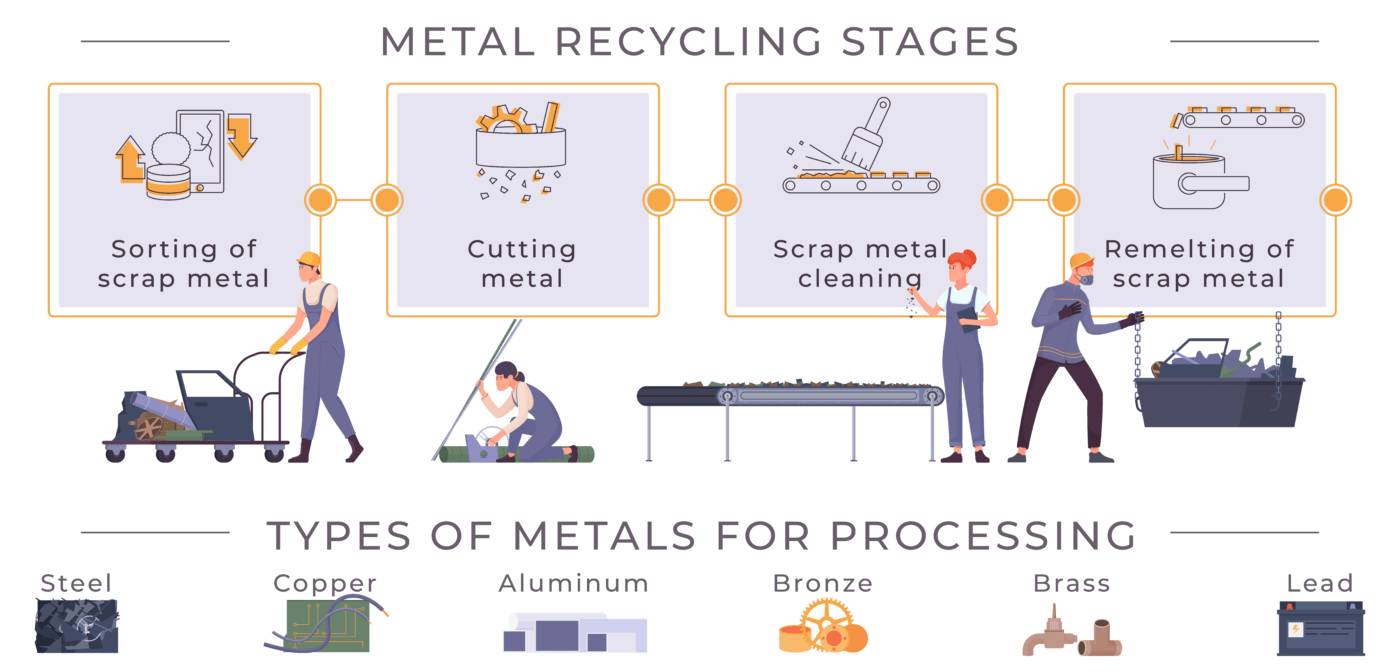
The steel recycling process involves melting down scrap steel and reforming it into new steel products—car parts, appliances, construction materials, and more! This can be done almost an infinite number of times, as recycling doesn’t compromise the quality or strength of the steel. Recycling steel not only conserves resources but also helps reduce waste and landfill space.
But its benefits don’t stop there! Recycling steel can generate additional revenue for your business. A quick Google search can show you where your local scrap buy-back location is and they’ll pay to take those worn knives off your hands!
To recap:
- Steel products can be recycled repeatedly without loss of strength
- The steel industry’s largest source of raw material is scrap metal, which is commonly collected by recycling steel
- Steel’s magnetic properties make it one of the easiest materials to separate from the solid waste stream
- Nearly 90% of all the steel produced globally each year is recycled – more than paper, aluminum, plastic and glass combined
- The steel industry has been recycling for over 150 years
While this resource is not renewable, the recyclability of steel and the widespread adoption of recycling practices contribute to its sustainability and reduce its environmental impact.
Don’t just toss those old, worn-out knives into the trash bin – set them aside in a scrap bin to be recycled. It’s good for you and it’s good for the environment too!
Frequently Asked Questions about Steel Recycling
Recycling steel, including industrial blades, offers several benefits. It helps conserve natural resources, reduces energy consumption, and decreases greenhouse gas emissions. By recycling steel, you can contribute to a circular economy and demonstrate your commitment to sustainability.
- Yes, recycled steel can achieve the same quality as virgin steel. Steel is a highly recyclable material, and advanced technologies ensure that recycled steel maintains its structural integrity and performance characteristics. Proper sorting, cleaning, and processing techniques in steel recycling facilities help maintain quality standards.
Steel recycling is subject to regulations and guidelines that vary by region. It is essential to comply with local environmental regulations, waste management protocols, and workplace safety standards. We recommended researching your local, reputable recycling facilities and seeking their guidance on those regulations to ensure your business complies.
To maximize steel recovery from your manufacturing processes, implement waste management practices that prioritize segregation and collection of steel scrap-including industrial blade. Provide dedicated containers throughout your facilities for steel scrap and educate employees on proper disposal procedures. Collaborate with the recycling partner you choose to assist in optimizing the recovery and recycling of steel from your operations.
Recycling industrial blades can lead to substantial cost savings for manufacturers. Recycling steel requires less energy compared to producing steel from scratch, resulting in reduced production costs. Additionally, recycling programs may offer incentives or rebates, further lowering expenses.
While steel recycling offers numerous benefits to manufacturers, there are some limitations and challenges to consider. These may include:
- Contamination: Steel scrap may contain contaminants, such as paints, coatings, or other metals. Proper sorting and cleaning are necessary to maintain the quality of recycled steel.
- Alloy-specific considerations: Certain steel alloys used in industrial blades may require specialized recycling processes, which can pose challenges in terms of availability and cost-effectiveness.
- Infrastructure and logistics: Access to efficient collection systems and transportation networks for steel scrap can be challenging, particularly for manufacturers located in remote areas or lacking well-established recycling infrastructure.
Integrating steel recycling into your manufacturing operations requires a proactive approach and a commitment to sustainability. Consider the following steps:
- Waste management assessment: Evaluate your manufacturing processes to identify opportunities for steel recycling. Determine the types and quantities of steel scrap generated and explore ways to collect and segregate it efficiently.
- Internal recycling programs: Implement internal recycling programs within your facility. Provide dedicated containers for steel scrap, label them clearly, and train employees on proper segregation practices.
- Partner with recycling facilities: Establish partnerships with reputable recycling facilities or scrap metal dealers that specialize in steel recycling. Collaborate to develop streamlined collection, transportation, and processing systems to ensure effective recycling of industrial blades and other steel scrap.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly review and refine your recycling processes. Monitor waste generation, recycling rates, and overall sustainability performance. Encourage employee involvement and foster a culture of environmental responsibility.
Various incentives and programs exist to support and encourage steel recycling initiatives. These may include:
- Government incentives: Check with local, regional, or national authorities for potential grants, tax incentives, or funding opportunities available for implementing recycling programs. These incentives can help offset the costs associated with steel recycling.
- Recycling industry initiatives: Collaborate with industry associations or recycling organizations that promote steel recycling. They may offer guidance, resources, and support for implementing and optimizing recycling practices.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs: In some regions, EPR programs place responsibility on manufacturers to manage the lifecycle of their products, including their end-of-life disposal. Explore whether such programs exist in your area and assess how they can support your steel recycling efforts.
- Certification programs: Look for certifications, such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems), which demonstrate your commitment to sustainable practices. Certification can enhance your reputation, attract environmentally conscious customers, and potentially open doors to additional incentives.
Common steel recycling processes include electric arc furnace (EAF) and basic oxygen furnace (BOF). EAF involves melting the steel scrap using electricity, while BOF utilizes oxygen to remove impurities from the molten steel. Both processes can effectively recycle industrial blades and other steel scrap.
Related Resources from Each of our Businesses:
TGW International
- Extend the Life of Poultry Processing Blades
- What Causes Packaging Blades to Fail and How to Prevent Blade Failure
- Understanding Industrial and Steel Blade Coating Options
Pearl Technologies Inc.
- Best Practices for Extending the Life of Your Steel Punches
- Pearl’s Rotary Blades, Cut-Off Blades and Bagger Knives for Packaging Processes